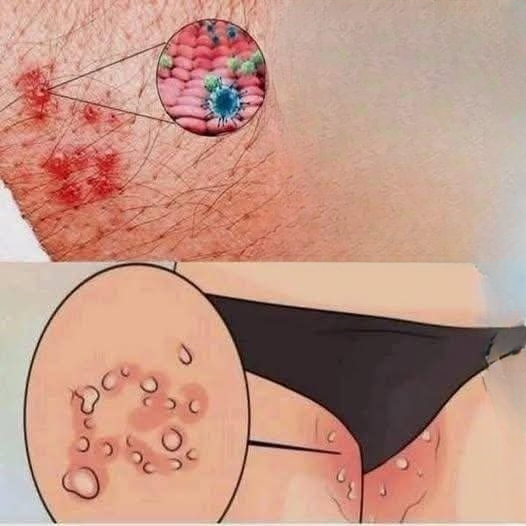
Skin discomfort in the groin area is a common issue that affects people of all ages, body types, and lifestyles. Because this part of the body is naturally warm, often moist, and subject to friction, it is particularly vulnerable to a range of skin concerns. While groin irritation can be uncomfortable or even distressing, most causes are not serious and can be treated effectively once properly identified.
Understanding what may be happening—and how to respond safely—can help prevent unnecessary worry, discomfort, or complications. This article explores the most common causes of groin skin irritation, how to recognize them, and practical steps you can take to support healing and prevent future problems.
Why the Groin Area Is Prone to Skin Problems
The groin is a sensitive region where several factors come together:
-
Constant movement and friction
-
Heat and moisture retention
-
Hair growth and hair removal
-
Close contact with clothing
-
Skin folds that reduce airflow
These conditions can disrupt the skin’s natural barrier, making it easier for irritation, inflammation, or infection to develop. Even people with otherwise healthy skin may experience groin-related issues from time to time.
1. Ingrown Hairs
What They Are
Ingrown hairs occur when a hair grows sideways or curls back into the skin rather than emerging normally. This can lead to small bumps that resemble pimples and may feel itchy or tender. In some cases, the area can become inflamed or infected.
Why They Happen
Ingrown hairs are particularly common in the groin due to hair texture and grooming habits. Common contributing factors include:
-
Shaving too closely or against hair growth
-
Waxing or plucking hair
-
Naturally curly or coarse hair
-
Tight clothing that increases friction
-
Dead skin cells blocking hair follicles
Common Symptoms
-
Small red or flesh-colored bumps
-
Mild to moderate itching
-
Swelling or tenderness
-
Occasionally, pus-filled bumps
How to Manage Ingrown Hairs
Most ingrown hairs improve on their own with gentle care. Helpful steps include:
-
Applying warm compresses to reduce inflammation
-
Gently exfoliating with a mild cleanser
-
Avoiding shaving until the skin heals
-
Wearing loose, breathable clothing
If ingrown hairs become painful, infected, or persistent, a dermatologist can recommend targeted treatments.
2. Folliculitis
What It Is
Folliculitis is inflammation of hair follicles, often caused by bacteria, fungi, or irritation. It appears as small red bumps or white-headed spots around hair follicles and can resemble acne.
Causes
Folliculitis may develop due to:
-
Bacterial growth, particularly Staphylococcus species
-
Frequent shaving or waxing
-
Tight clothing that rubs against the skin
-
Hot tubs or pools that are not properly cleaned
-
Excessive sweating
Symptoms
-
Red or white bumps around hair follicles
-
Mild itching or burning
-
Tenderness in the affected area
-
Occasionally, crusting or drainage
Treatment Options
Mild cases often improve with simple care:
-
Washing the area gently with antibacterial soap
-
Applying warm compresses
-
Avoiding shaving during healing
More persistent or severe cases may require prescription treatments from a healthcare provider.
3. Fungal Infections of the Groin (Often Called Jock Itch)
What It Is
A common fungal condition affecting the groin is known as tinea cruris. It thrives in warm, damp environments and can spread easily if untreated.
Risk Factors
-
Excessive sweating
-
Tight or non-breathable clothing
-
Sharing towels or clothing
-
Prolonged moisture exposure
-
Inadequate drying after bathing
Recognizable Signs
-
Red or darkened patches with defined edges
-
Scaling or flaking skin
-
Persistent itching or burning
-
Rash that may spread to nearby areas
Effective Management
Treatment typically includes:
-
Over-the-counter antifungal creams
-
Keeping the area clean and dry
-
Wearing loose, breathable underwear
-
Avoiding shared personal items
Consistency is key, as fungal infections may return if treatment is stopped too early.
4. Contact Dermatitis
What It Is
Contact dermatitis is a skin reaction caused by exposure to an irritant or allergen. The groin area is particularly sensitive to products that come into direct contact with the skin.
Common Triggers
-
Scented soaps or body washes
-
Laundry detergents with strong fragrances
-
Synthetic fabrics
-
Latex or elastic materials
-
Personal care products
Symptoms
-
Redness and irritation
-
Itching or burning
-
Dry, flaky, or peeling skin
-
Small blisters in more severe cases
How to Treat It
-
Identify and avoid the trigger
-
Switch to fragrance-free, gentle products
-
Use soothing moisturizers
-
Apply mild topical creams if recommended
If symptoms persist, professional evaluation can help identify specific allergens.
5. Intertrigo
What It Is
Intertrigo is an inflammatory condition that develops in skin folds, including the groin. It occurs due to friction, trapped moisture, and limited airflow.
Who Is at Higher Risk
-
People who sweat heavily
-
Individuals with skin folds
-
Those wearing tight or non-breathable clothing
-
People who are overweight
Symptoms
-
Red, raw-looking skin
-
Burning or stinging sensation
-
Unpleasant odor
-
Possible secondary infection
Management Strategies
-
Keep the area dry using absorbent powders
-
Apply barrier creams to reduce friction
-
Address any fungal or bacterial overgrowth
-
Improve airflow with loose clothing
Preventive Care: Reducing the Risk of Groin Irritation
Preventing groin skin problems often comes down to daily habits. The following practices can significantly reduce irritation:
1. Practice Gentle Grooming
-
Use clean, sharp razors
-
Shave in the direction of hair growth
-
Avoid dry shaving
-
Consider trimming instead of shaving
2. Choose Breathable Clothing
-
Wear cotton or moisture-wicking underwear
-
Avoid tight-fitting garments
-
Change clothes after sweating
3. Maintain Proper Hygiene
-
Clean the area daily and after physical activity
-
Dry thoroughly after bathing
-
Avoid over-washing, which can irritate skin
4. Use Mild Products
-
Choose fragrance-free soaps and detergents
-
Avoid harsh chemicals or scrubs
-
Test new products on a small area first
5. Avoid Sharing Personal Items
-
Do not share towels, razors, or clothing
-
Wash items regularly in hot water
When to Seek Medical Advice
While many groin skin issues are mild and manageable at home, professional care is important if:
-
Symptoms last longer than two weeks
-
Pain, swelling, or discharge develops
-
Fever or general illness occurs
-
The rash spreads rapidly or keeps returning
A healthcare provider can identify the exact cause and recommend appropriate treatment.
Emotional and Quality-of-Life Considerations
Groin skin conditions can affect more than physical comfort. Many people experience embarrassment, stress, or anxiety related to symptoms. It’s important to remember that these conditions are extremely common and not a reflection of poor hygiene or personal habits.
Seeking timely care and practicing self-compassion can help reduce both physical and emotional discomfort.
Final Thoughts
Groin irritation is a widespread and manageable issue. From ingrown hairs and folliculitis to fungal infections and contact dermatitis, most causes are treatable with proper care, awareness, and prevention.
The key is early attention, gentle hygiene, breathable clothing, and avoiding known irritants. When symptoms persist or worsen, professional guidance ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Taking care of your skin is an essential part of overall health—and with the right approach, groin skin concerns can be resolved safely and confidently.