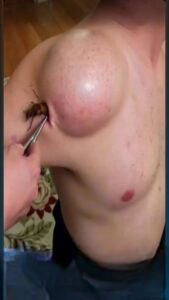
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions worldwide, affecting millions of people across different age groups. While occasional breakouts are normal, certain types of acne can signal an underlying medical issue or require specialized care. Knowing when to consult a dermatologist can significantly improve outcomes, prevent scarring, and help maintain healthy skin.
Understanding Acne: More Than Just Pimples
Acne is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. It often appears on the face, back, chest, and shoulders, though it can occur elsewhere on the body. While many people experience mild, occasional pimples, severe forms of acne can have a lasting impact on physical appearance and mental health.
Common Types of Acne
-
Comedonal Acne: Includes blackheads and whiteheads; generally mild and non-inflammatory.
-
Inflammatory Acne: Includes papules and pustules that are red, swollen, and sometimes painful.
-
Nodular and Cystic Acne: Deep, painful lesions under the skin that can lead to scarring.
It is especially important to consult a dermatologist if acne is severe, persistent, or accompanied by nodules or cysts, as these forms require specialized medical treatment.
Signs You Should See a Dermatologist
Dermatologists are medical professionals who specialize in diagnosing and treating skin conditions, including acne. Here are key indicators that it may be time to seek professional care:
1. Cysts and Nodules
Cysts are large, pus-filled lesions deep under the skin, while nodules are hard, painful bumps caused by inflammation. Both can cause permanent scarring if untreated. Patients with cystic or nodular acne benefit from prescription medications or procedures that can reduce inflammation and promote healing.
2. Painful or Deep Acne
When acne causes significant discomfort or interferes with daily life, it is advisable to see a dermatologist. Painful acne may indicate a severe inflammatory response that over-the-counter treatments cannot resolve.
3. Late-Onset Acne
Late-onset acne refers to acne appearing in adults who have never experienced significant breakouts before. This type of acne can be linked to hormonal changes, stress, diet, or underlying health issues. Because it is unusual, a dermatologist can perform tests to determine the cause and recommend effective treatment.
4. Persistent Acne
Persistent acne is a continuation or recurrence of acne from adolescence into adulthood. People with persistent acne often struggle with scarring, pigmentation, and emotional distress. Early intervention by a dermatologist can help control symptoms and prevent long-term damage.
Causes of Acne in Adults
Acne in adulthood can result from a variety of factors, often in combination:
1. Hormonal Changes
Hormones play a significant role in acne development. In women, hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, menopause, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can trigger breakouts. Men can also experience acne flare-ups due to androgen-related increases in oil production.
2. Genetics
Genetics influence skin type, oil production, and susceptibility to inflammation, which can increase the likelihood of developing acne, particularly persistent or nodular forms.
3. Lifestyle Factors
-
Diet: High-glycemic foods, dairy products, and processed foods may contribute to breakouts in susceptible individuals.
-
Stress: Elevated stress levels can lead to increased hormone production, aggravating acne.
-
Skincare routines: Using harsh products or improperly cleansing skin can worsen acne.
4. Medications
Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, lithium, and some anticonvulsants, may trigger acne. Dermatologists can evaluate medication-related causes and adjust treatment accordingly.
Potential Complications of Untreated Acne
Ignoring severe or persistent acne can lead to a variety of physical and psychological complications:
-
Scarring: Deep nodules and cysts can leave permanent marks.
-
Hyperpigmentation: Dark spots may linger long after acne lesions heal.
-
Infections: Scratching or picking can introduce bacteria, causing secondary infections.
-
Emotional Impact: Acne can lead to anxiety, low self-esteem, and social withdrawal.
Professional intervention helps reduce these risks, providing not only clearer skin but also improved mental well-being.
How Dermatologists Treat Acne
Dermatologists employ a variety of treatment strategies tailored to the type and severity of acne:
1. Topical Treatments
-
Retinoids: Promote cell turnover and prevent clogged pores.
-
Antibiotics: Reduce bacterial growth and inflammation.
-
Benzoyl Peroxide: Targets acne-causing bacteria and excess oil.
2. Oral Medications
-
Antibiotics: For moderate to severe acne resistant to topical treatments.
-
Hormonal Treatments: Birth control pills or anti-androgen medications for women with hormonal acne.
-
Isotretinoin: A potent medication for severe nodular or cystic acne, often used when other treatments fail.
3. Procedural Treatments
-
Chemical Peels: Exfoliate the skin and unclog pores.
-
Laser Therapy: Reduces inflammation, kills bacteria, and improves scarring.
-
Drainage and Extraction: Removes large cysts or nodules safely.
Dermatologists often combine multiple treatments for optimal results, monitoring patients closely for side effects and efficacy.
Skincare and Lifestyle Tips
Even with professional care, lifestyle and daily skincare play a vital role in managing acne:
-
Gentle Cleansing: Use mild, non-comedogenic cleansers twice daily.
-
Moisturizing: Hydration supports skin barrier function and reduces irritation.
-
Sun Protection: Sunscreen prevents hyperpigmentation and protects sensitive skin.
-
Healthy Diet: Balanced nutrition with low-glycemic foods may reduce flare-ups.
-
Stress Management: Mindfulness, exercise, and adequate sleep can positively affect skin health.
A dermatologist can provide personalized recommendations based on skin type, acne severity, and lifestyle.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Certain acne symptoms require urgent dermatologic evaluation:
-
Rapidly spreading cystic acne or painful nodules.
-
Signs of infection, such as pus, redness, or swelling beyond typical inflammation.
-
Acne accompanied by hormonal irregularities or systemic symptoms.
Early intervention prevents complications and allows targeted treatment plans for faster recovery.
Psychological Benefits of Professional Acne Care
Acne is not just a cosmetic concern — it affects mental health and social well-being. Seeing a dermatologist and achieving effective control can:
-
Improve self-esteem and confidence.
-
Reduce anxiety related to appearance.
-
Provide a structured approach to long-term skin care.
Patients often report higher satisfaction and quality of life when acne is managed proactively with medical guidance.
Summary
Acne is a complex condition influenced by hormones, genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors. While mild breakouts may be managed at home, cysts, nodules, painful acne, late-onset, or persistent cases warrant professional care. Dermatologists offer a wide range of treatments — from topical and oral medications to procedural interventions — tailored to individual needs.
Early consultation not only prevents scarring and physical complications but also supports mental well-being and overall quality of life. For anyone struggling with severe or persistent acne, seeing a dermatologist is a crucial step toward achieving clear, healthy skin and restoring confidence.
Key Takeaways
-
Severe or painful acne should be evaluated by a dermatologist.
-
Late-onset acne may indicate hormonal or medical issues.
-
Persistent acne requires long-term management strategies.
-
Dermatologists offer medications, procedures, and lifestyle guidance.
-
Early intervention prevents scarring and psychological impact.
By understanding the signs, causes, and treatments for acne, patients can make informed decisions, take proactive steps, and achieve lasting skin health.